Plantain and banana trees are difficult to distinguish because, even in their vegetative stage, they seem extremely similar. The easiest way to tell the difference between the two trees is to look at their fruits and physical traits.
One could ask what the difference between a banana plant and a banana plant is based solely on appearance. However, while the two may appear to be identical, the flavour of a banana is not to be confused with that of a banana.
Bananas, sometimes known as bananas or bananas, are a mainstay in many families. They are sweet and soft fruits that are widely consumed, although bananas are not.
The differences between bananas and bananas are discussed in this article.
What Is the Difference Between Plantains and Bananas?
Banana
The edible fruits produced by a range of big herbaceous plants of the genus Musa are known as bananas (that is, a stem without woody tissue). The banana is classified as a berry in botanical terms.
Despite their origins in Southeast Asia, banana plants are frequently employed in European and North American cuisine.
They have a thin body, are long, and have thick fur to protect them.
It comes in a variety of shapes and sizes, and they yield a variety of fruits. However, in Western countries, the word “banana” usually refers to the sweet, yellow kind.
When immature, the outer skin is green, stiff, and difficult to pull off.
As you become older, your skin turns light yellow, then dark brown. It’s also simple to remove.
The fruit can be eaten raw or cooked, and the edible pulp of the fruit becomes sweeter, darker, and softer as it ripens.
Plantain
The term “banana” refers to a type of banana that has an entirely different flavour and application profile from the common sweet yellow banana.
Bananas, like bananas, are native to Southeast Asia. They are, however, grown all over the world, including Egypt, Indonesia, India, and the tropical regions of America.
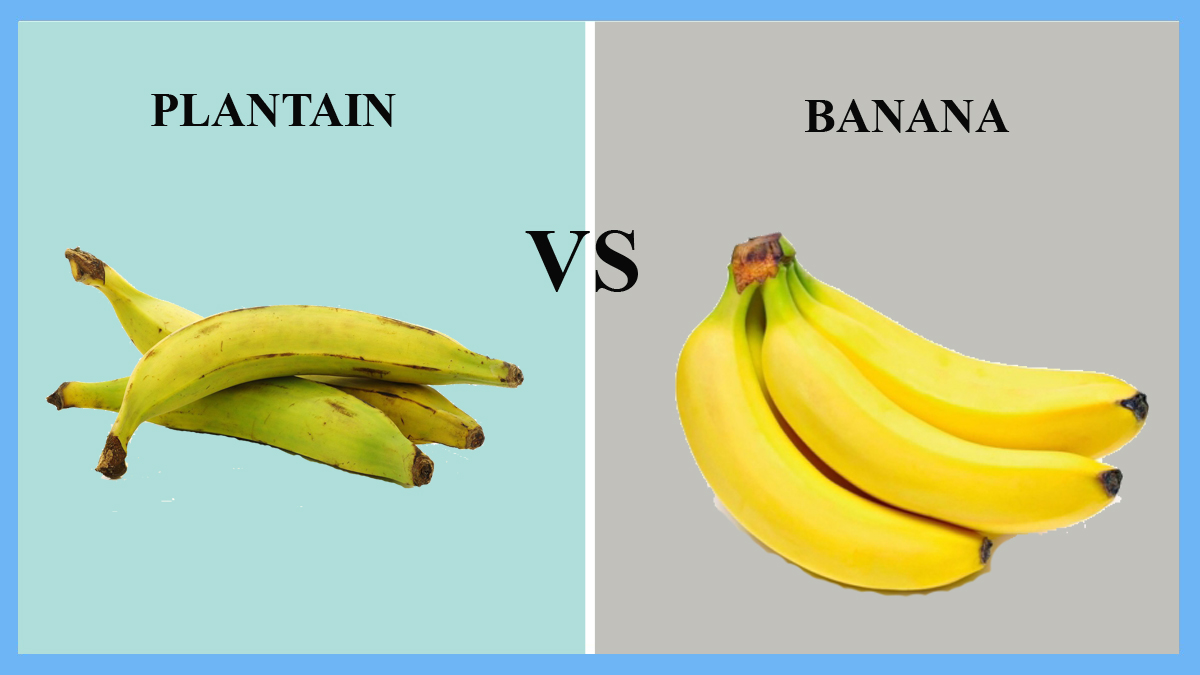
Bananas are often larger, tougher, and have a thicker skin. They come in a variety of shades, including green, yellow, and very dark brown.
Bananas are rarely eaten fresh due to their high carbohydrate content and must be cooked (boiled, roasted, fried, or baked) before consumption.
| Plantain | Banana | |
| Definition | Plantain is a type of banana that is normally not consumed raw due to its slightly sweet flavor. The Musaceae family includes both bananas and plantains. | Banana is a well-known fruit that comes from the tall grass that is commonly referred to as a banana tree or plant. |
| Size | Long | Comparatively Short |
| Skin | Thicker | Comparatively Thinner |
| Starch Content | Comparatively More | Comparatively Less |
| Usually Eaten | Cooked | Raw |
| Common Color | Pale Yellow | Green or Yellow |
| Moisture Content | Little Humid | It’s Very Humid |
| Skin to Pulp Ratio | Higher | Comparatively Less |
These are some of the features that set bananas apart from plantains.
Take a look at the plant’s leaves. While the colour of the leaves of plantain and banana plants varies, the form of the leaves can sometimes be used to distinguish between them.
Banana leaves are similar in shape to shoe soles, however they are more tubular and longer.
Examine the plant’s fruit form. Bananas are yellow when mature and around 6 inches long, whereas green or black bananas are about 12 inches long.
Feel the texture of the plant’s fruit with your hand. Bananas have a medium-thick skin that is softer than bananas, which have a hard, thick skin.
Conclusion
Because of their strong visual similarities, plantain plants and banana plants are easily confused.
However, after eating the fruits, it’s easy to tell the difference.
Check the shape of the leaves and the form of the appropriate fruit on each plant to see the differences between plantains and bananas.
Aside from that, their nutritional composition and potential health benefits are identical, but not their suckers.
Bananas have more sugar than bananas but less starch. They work best in savoury recipes, whereas bananas work well in desserts or on their own.
Fruits are nutritious and healthy foods and can be consumed as part of a healthy diet.






